System Design: Building & Scaling to 100 million
Users
1
Single Server Setup......................................................................................................................... 2
1.1 Database.................................................................................................................................. 3
1.1.1 Database: SQL vs NoSQL..................................................................................................... 3
1.1.2 Data warehouse vs Data Lake.............................................................................................. 4
2 Understand bottlenecks.................................................................................................................. 5
3 Upscale: Multiple Server Setup........................................................................................................ 5
3.1 Vertical Scaling vs horizontal scaling........................................................................................... 5
3.1.1 Vertical Scaling.................................................................................................................... 5
3.1.2 Horizontal Scaling................................................................................................................ 6
3.2 Load balancer........................................................................................................................... 6
3.2.1 Load balancing algorithms................................................................................................... 7
3.3 Database.................................................................................................................................. 7
3.3.1 Database replication(Master/Slave).................................................................................... 7
3.3.2 Database partitioning/sharding........................................................................................... 8
3.4 Cache....................................................................................................................................... 8
3.4.1 Cache tier........................................................................................................................... 9
3.4.2 Considerations for using cache............................................................................................ 9
3.5 Content delivery network (CDN)............................................................................................... 9
3.6 Stateless web tier..................................................................................................................... 9
3.6.1 Stateful vs Stateless Architecture........................................................................................ 9
3.6.2 Stateless architecture....................................................................................................... 10
4 Global Multiple Data center........................................................................................................... 10
5 Traditional vs Cloud computing....................................................................................................... 11
5.1 Cost, Time, and Security.......................................................................................................... 11
5.2 Management cost................................................................................................................... 12
6 Message queue............................................................................................................................. 12
7 Logging, metric, automation........................................................................................................... 12
8 Summary....................................................................................................................................... 13
9 Reference..................................................................................................................................... 13
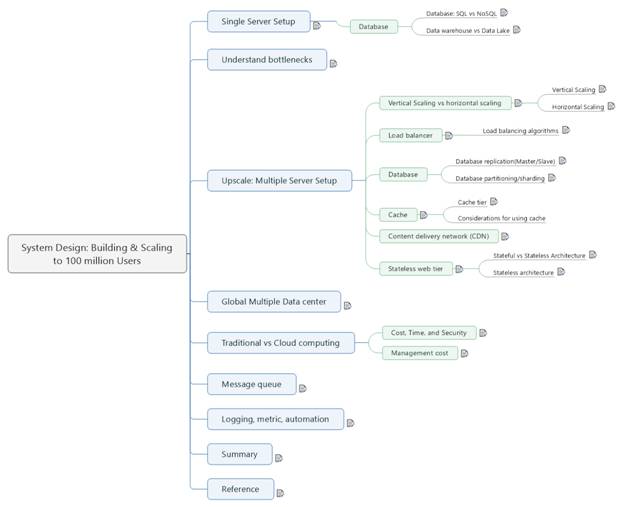
single
server setup is where everything is running on one server: web server, app,
database, cache, etc.
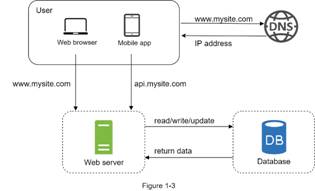
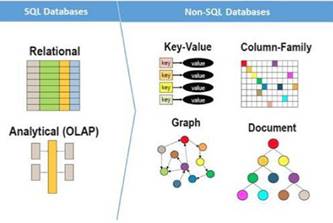
- SQL(relational database) are the most popular database, SQL
store data in tables and rows. We can perform join operations using SQL across
different datable tables.
most popular SQL database are MySQL, Oracle database,
PostgreSQL, etc.
- NoSQL(Non-relational database) group data into four
categories: key-value stores, graph stores, column stores, and document stores.
Join operations are generally not supported in non-relational databases.
most popular Non-relational database are CouchDB, Neo4j,
Cassandra, HBase, Amazon DynamosDB, etc.
For most project, SQL database the best option because it
been around for 40 years and it work well; However, No-SQL may be a good choice
if:
- your application requires super-low latency.
- You need to store a massive amount of data.
- your data is unstructured, or you do not have any relational data.
- You only need serialize and deserialize data (XAML, JSON, YAML, etc)
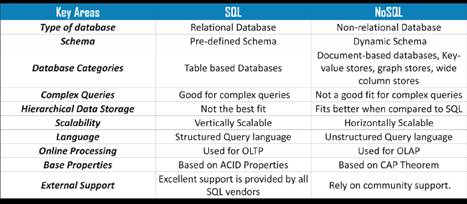
1.1.2 Data
warehouse vs Data Lake
|
|
DATA WAREHOUSE |
DATA LAKE |
|
DATA |
Structured, processed |
structured, semi-structured, unstructured, raw |
|
SCALE |
Scales to moderate volume at a high cost |
Scales to huge volumes at low cost |
|
PROCESSING |
schema-on-write |
schema-on-read |
|
STORAGE |
expensive for large data volumes |
designed for low-cost storage |
|
AGILITY |
less agile, fixed configuration |
Highly agile, configure and reconfigure as needed |
|
SECURITY |
mature |
maturing |
|
USERS |
business professional |
data scientist, data analytic |
- How your system perform if they number of
users increase by 10X, 100X, or 1000X?
- What if a component in your system failed?
- Is the database too slow and does it need some in-memory caching?
- Perhaps your system needs a load balancer and many machines behind it to
handle the user request. Or maybe the data is so huge that you need to
distribute your database on multiple machines. What are some of the downsides
that occur from doing that?
3 Upscale:
Multiple Server Setup
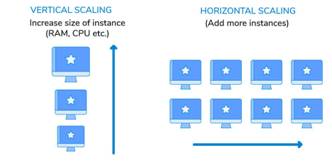
3.1 Vertical
Scaling vs horizontal scaling
- Vertical scaling is
adding more power (CPU, RAM) to your existing machine, Horizontal scaling is
add more machine into your pool of resources.
Advantages
of vertical scaling:
- Most
of the software can easily take advantage of vertical scaling.
- Less power consumption than running multiple servers.
- Easy to manage and install hardware within a single machine.
Disadvantages
of vertical scaling:
-
Requires huge amount of financial investment.
- Greater risk of hardware failure causing bigger outages.
- Generally vendor lock-in and limited upgradeability in future.
- Low availability.
- There is hardware limit.
Advantages
of horizontal scaling:
- Much
lower cost than vertical scaling.
- Easier to run fault-tolerance.
- Ability to scale out as much as possible.
- High availability.
Disadvantages
of horizontal scaling:
-
Software has to handle all the data distribution and parallel.
- Limited number of software are available that can take advantage of
horizontal scaling.
- Higher utility cost (electricity and cooling).
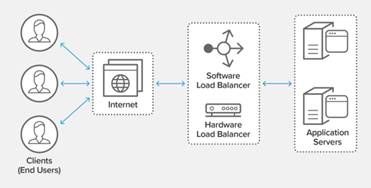
Load balancing is a technique to distributing incoming
network traffic across a group of backend servers, also know as a server farm
or server pool. The benefit of load balancing is reduced downtime, scalable,
redundancy, flexibility, efficiency.
3.2.1 Load
balancing algorithms
1) Round Robin: Requests are distributed across the group of
servers sequentially.
2) Least Connections: A new request is sent to the server
with the fewest current connections to clients. The relative computing capacity
of each server is factored into determining which one has the least
connections.
3) Least Time: Sends requests to the server selected by a
formula that combines the
fastest response time and fewest active connections.
Exclusive to NGINX Plus.
4) Hash: Distributes requests based on a key you define, such
as the client IP address or
the request URL. NGINX Plus can optionally apply a consistent
hash to minimize redistribution
of loads if the set of upstream servers changes.
5) IP Hash: The IP address of the client is used to determine
which server receives the request.
6) Random with Two Choices: Picks two servers at random and
sends the request to the
one that is selected by then applying the Least Connections
algorithm (or for NGINX Plus
the Least Time algorithm, if so configured).
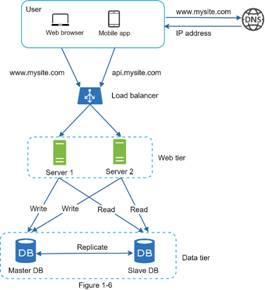
3.3.1 Database
replication(Master/Slave)
Database
replication is create one or more copy of your database, so that all users
share the same level of information. The result is a distributed database in
which users can access data relevant to their tasks without interfering with
the work of others. The implementation
of database replication for the purpose of elimination data ambiguity or
inconsistency among users is known as normalization.
- All write actions (Create, Update, Delete) will be done to the
"master", all the read actions will be done on the "slave".
- If any of "slave" go down, we can create new "slave"
easily. If the "master" go down, one of the "slave" will
promote to master.
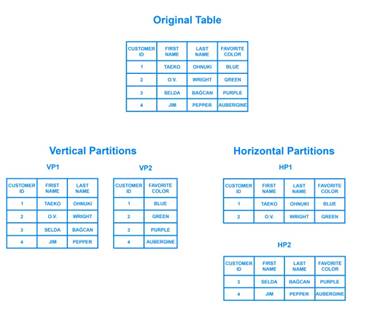
3.3.2 Database
partitioning/sharding
Partitioning
of relational data usually refers to decomposing your tables either row-wise
(horizontally) or column-wise (vertically).
Cache is the temporary storage area that stores the result of
expensive responses or frequently accessed data in memory so that subsequent
requests are served more quickly.
Cache tier is a temporary data store layer, much faster than
the database, it help improve system performance and reduce database workloads.
3.4.2 Considerations
for using cache
3.5 Content
delivery network (CDN)
CDN is a network of geographically dispersed servers used to
deliver static content, it cache static content like images, video, CSS,
JavaScript files, etc.
Thing
to consider when use CDN:
- Cost:
CDN are run by third-party providers, and we are charged for data transfers in
and out of the CDN. Caching infrequently used data may provide little to no
benefits.
- Expiration: setting an appropriate cache expiry is important. if the cache
expiry time is too long, the content no longer fresh, if the cache expiry time
is too short, it can cause repeat load of content from server to CDN.
- CDN fallback: how our website deal with the failure of CDN's server, clients
should be able to detect the problem and request resource from original server.
State is the user session data, by move the user session data
out of the web tier and store it in persistent storage such as SQL or NoSQL, we
allow each web server in the cluster to access state data. This is called
"stateless web tier"
3.6.1 Stateful vs
Stateless Architecture
A stateful server remembers client data from one request to
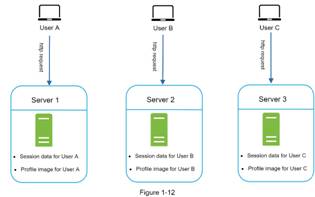
the next. A stateless server keeps no state information.
in stateful server, router will route user A to server 1, user B to server 2,
and user C to server 3. The issue is that every request from same client must
be route to the same server, this can be done with sticky sessions in most load
balances; however this create overhead, adding or removing servers is much more
difficult and it is challenge to handle server failure.
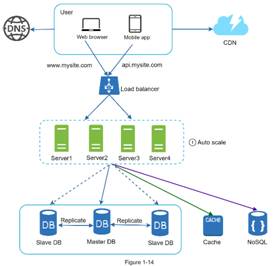
in stateless architecture, requests from a user can be sent
to any servers, each server will access state data from shared data store.
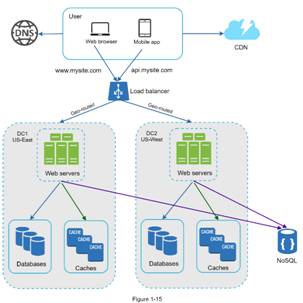
To handle a
large number of user globally, we can build several data center around the
world, and users are GeoDNS-routed to closest data center.
Several key
technique to consider for global data center:
1) traffic
redirection: effective tools are needed to direct user to the nearest data
center.
2) Data synchronization: users from different GeoDNS could use different local
databases or caches.
5 Traditional
vs Cloud computing
|
|
Cloud
Computing |
Traditional
Computing |
|
Security |
Someone else’s data
centers |
In-house data center |
|
Upfont cost |
Low upfront infrastructure investment |
High Upfront costs |
|
Scalability |
Scalable quickly |
Slow Scaling |
|
Efficient |
Efficient resource ultilization |
Lower efficiency |
|
Cost |
Pay-as-you-go |
Higher Cost |
A message
queue is queue of message sent between applications, it includes a sequence of
work that waiting to be processed.
the basic architecture of message include an "input services", called
producer/publishers, create messages, and the other services or server, called
consumers/subscribers, connect to the queue and perform actions defined by the
messages.

Logging:
monitoring error logs to identify errors and problems in the system.
Metrics: use metric to gain an insight about the
health status of the system, for example:
- Host level metrics: CPU, Memory, Disk I/O
-
Aggregated level metric: the performance of entire database tier, cache tier,
etc.
- Key business metric: daily active users,
retention, revenue, etc.
Automation:
When a system gets big and complex, we need to use automation tools to improve
productivity. Continuous integration is good practice.
To handle
100 million users and beyond:
- max out the vertical scaling: using the fastest and best CPU/RAM/SSD
disks/RAM Disks.
- keep web
tier stateless.
- build
redundancy at every tier.
- cache data
as much as possible.
- Support
multiple data center around the world.
- Host
static assets in CDN.
- Scale you
data tier by partitioning/sharding.
- split
tiers into individual services.
- monitor
your system and use automation tools.
https://systeminterview.com/scale-from-zero-to-millions-of-users.php
https://medium.com/edureka/sql-vs-nosql-db-5d9b69ace6ac
https://www.thorntech.com/sql-vs-nosql/
https://www.redswitches.com/blog/difference-between-horizontal-vertical-scaling/
https://www.nginx.com/resources/glossary/load-balancing/
http://www.ines-panker.com/2019/08/03/scaling-1-to-10-000-users.html
http://www.ines-panker.com/2019/08/10/scaling-100-000-to-500-M-users.html
http://supplychaininstitute.com/data-lake-vs-data-warehouse-key-differences/
https://www.zaloni.com/resources/blog/why-smart-companies-are-complementing-their-data-warehouses-with-data-lakes/
https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Comparison-of-Cloud-Computing-models-in-terms-of-software-components-separation-of_fig2_327700356