Note
on Full-Stack Developer
Compiled by Linh Truong | Incomplete and will be updated
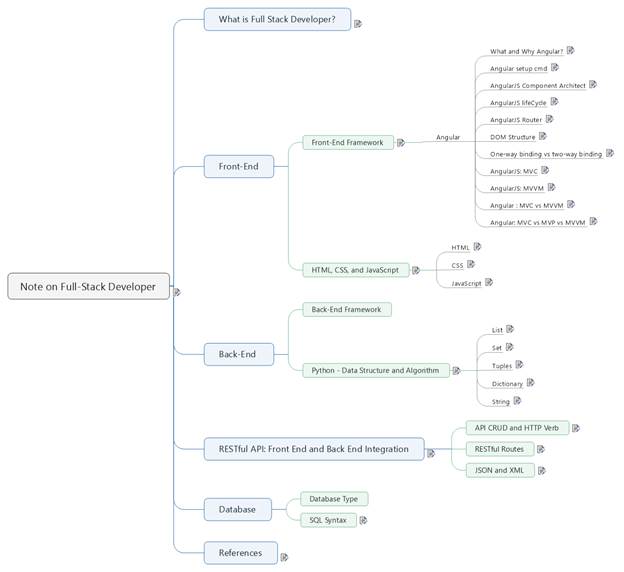
A What is Full Stack Developer?.................................................................................................... 3
B Front-End..................................................................................................................................... 4
B.1 Front-End Framework........................................................................................................... 4
B.1.1 Angular........................................................................................................................... 4
B.1.1.1 What and Why Angular?......................................................................................... 4
B.1.1.2 Angular setup cmd................................................................................................... 5
B.1.1.3 AngularJS Component Architect............................................................................. 6
B.1.1.4 AngularJS lifeCycle................................................................................................. 8
B.1.1.5 AngularJS Router.................................................................................................... 8
B.1.1.6 DOM Structure...................................................................................................... 10
B.1.1.7 One-way binding vs two-way binding................................................................... 11
B.1.1.8 AngularJS: MVC................................................................................................... 12
B.1.1.9 AngularJS: MVVM............................................................................................... 15
B.1.1.10 Angular : MVC vs MVVM................................................................................. 17
B.1.1.11 Angular: MVC vs MVP vs MVVM.................................................................... 23
B.2 HTML, CSS, and JavaScript............................................................................................... 23
B.2.1 HTML........................................................................................................................... 24
B.2.2 CSS............................................................................................................................... 28
B.2.3 JavaScript..................................................................................................................... 29
C Back-End................................................................................................................................... 31
C.1 Back-End Framework......................................................................................................... 31
C.2 Python - Data Structure and Algorithm.............................................................................. 31
C.2.1 List................................................................................................................................ 31
C.2.2 Set................................................................................................................................. 33
C.2.3 Tuples........................................................................................................................... 35
C.2.4 Dictionary..................................................................................................................... 36
C.2.5 String............................................................................................................................ 39
D RESTful API: Front End and Back End Integration................................................................. 42
D.1 API CRUD and HTTP Verb............................................................................................... 43
D.2 RESTful Routes.................................................................................................................. 44
D.3 JSON and XML.................................................................................................................. 44
E Database..................................................................................................................................... 46
E.1 Database Type..................................................................................................................... 46
E.2 SQL Syntax......................................................................................................................... 46
F References.................................................................................................................................. 48
A What is Full Stack Developer?
Full-Stack is a developer that can do both front-end and back-end, along with some knowledge about database and dev-ops.
Most of the time, the full-stack developer do not need to master all those skill-sets; however, he/she capable to learn it quickly to apply to the project when needed.
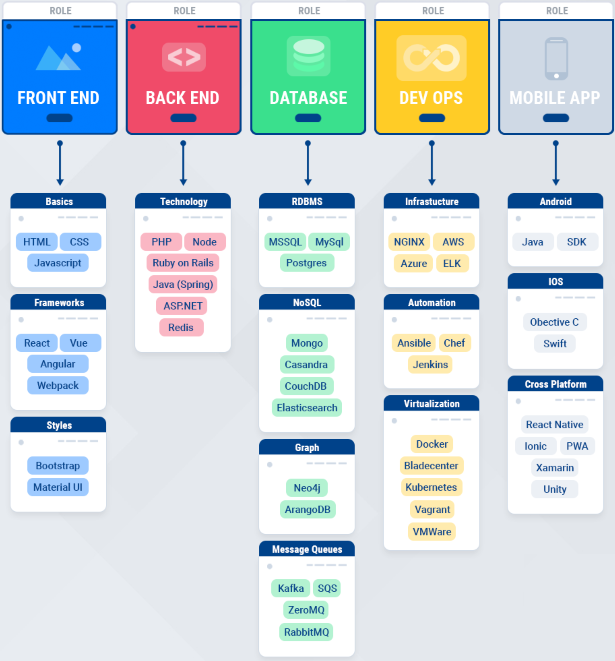
Some popular front-end frame work:
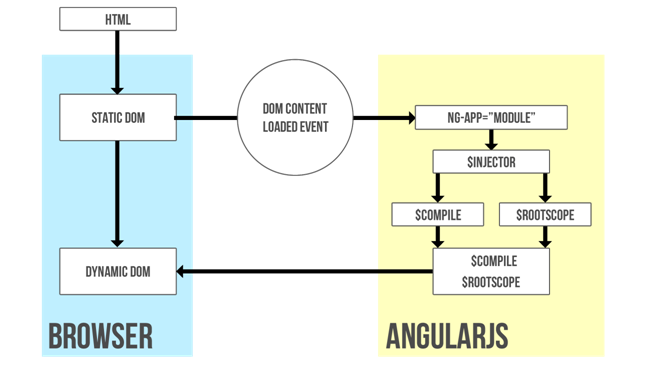
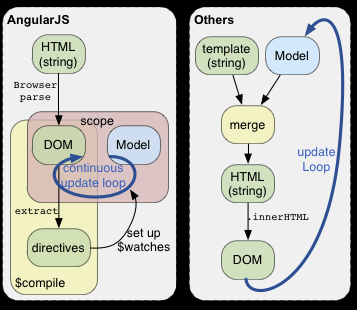
AngularJS is JavaScript-based open-source front-end web framework developed and maintained by Google. AngularJS using Single-Page-Applications(SPA) architect that load a single HTML page and dynamically update that page as the user interacts with the app.
- SPA works
and feels more like an application then a web page.
- SPA separates UI and data, SPA communicates with server only with JSON REST
API (Send/Receive JSON using AJAX)
- Reducing bandwidth usage is also a plus.
- SPA can use caching and local storage effectively.
- You can easily fake JSON data communication to test SPA, and you can also
fake JSON requests to server to write unit tests.
- Modular Structure: Angular organized code into buckets, whether it is
components, directive, pipes, or services.
- Allow lazy loading in background or on-demand.
- Simplified MVC or MVVM design pattern.
- Reusability: component-based structure of Angular makes the components highly
reusable across the app.
- Decoupled components makes it easier for maintenance and update.
1) Download and install Node.JS at nodejs.org
2) install the Angular CLI:
npm install -g @anglar/cli
3) create a workspace and initial application:
ng new my-app
4) Run the application :
cd my-app
ng serve --open
5) open browser at : http://localhost:4200/
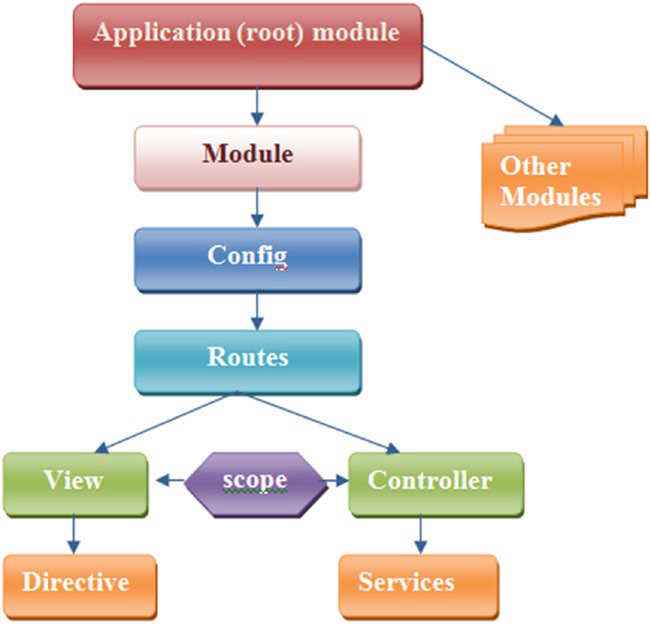
B.1.1.3 AngularJS Component Architect
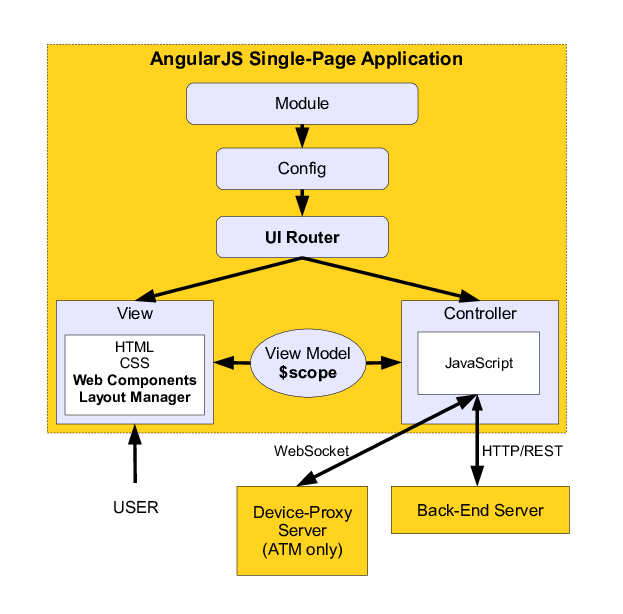
AngularJS allows developers to build structured applications based on the
MVC(or MVVM) model that are robust and easily maintained, so it is important to
understand the components architect.
Module:
A module iss a container contraining services, controllers, filters,
directives, and so on. Each module in AngularJs has it own folder structure for
controllers, directives, and so o. Each View page in AngularJS has a module.
Scope:
Scope in AngularJS is just a JavaScript representation of data used to populate
a view on a web page. This data can be from any source such as a database or a
remote web server.
View: Views with templates and directives in AngularJS are components to build an HTML view.
Expression: the ability to add an expression inside an HTML template. expression is basically linked to a scope helps bind application data to HTML.
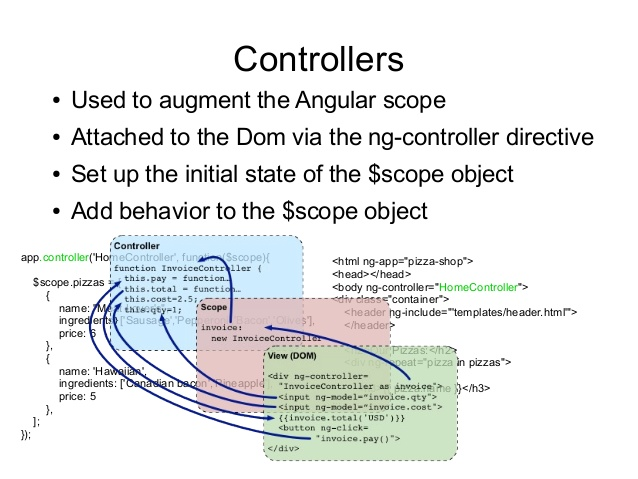
Controller: contain core business logic, connect Data to the View using scope
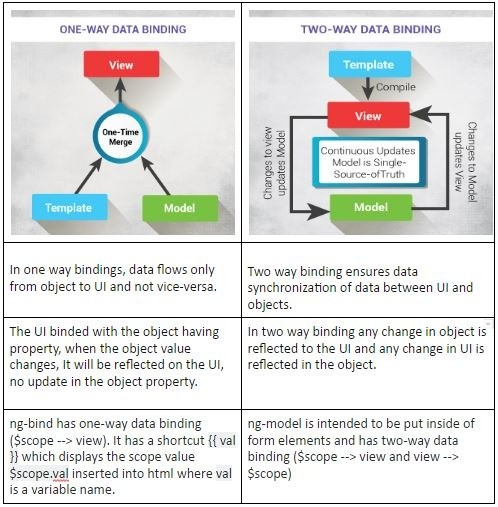
Data Binding: the process of linking data from the model to the view, and vice versa. AngularJS support two-way data binding.
- When data changes on the web page, the model is updates.
- when data changes in the model, then the view page is automatic updates.
Model: present the data and the view displace the data
Services: services in AngularJS are singleton objects that provide functionality for web application
Dependency Injection: DI is the process of injecting the dependency at runtime(i.e., making dependent components available for access within the component of initialized code). It is used to consume services. for example, if a module requires access to a resource via an HTTP request, then the HTTP service can be injected into the module to make the functionality available in the module code.
ngOnInit(): This is called when the component is loaded into the DOM and it occurs only once.
ngOnChanges(): This is called when there is Input property to the component and it is called before ngOnInit() and occurs every time there is a change in the input property. It is not called if there is no input property to the component
ngDoCheck(): occurs every time there is a change detection and immediately after ngOnChanges() and ngOnInit().
ngOnDestroy(): This is called right before the component gets destroyed and occurs only once.
ngAfterViewInit(): This is called once after the component’s view/ child views are loaded and right after ngAfterContentChecked() and occurs only once.
ngAfterViewChecked(): This is called after component’s view/ child views are loaded and called after ngAfterViewInit() and every time after ngDoCheck().
ngAfterContentInit(): This is called once external content is projected into component’s view and right after the first ngDoCheck() and occurs only once.
ngAfterContentChecked(): This is called after external content projected into component’s view and called after ngAfterContentInit() and every subsequent ngDoCheck().
Sample js/App.js for router
|
var app = angular.module('app',['ngRoute']);
app.config(function($routeProvider) { $routeProvider
//default page .when('/', { templateUrl : 'pages/homepage.html', controller : 'Homepage' })
//page2 .when('/about', { templateUrl : 'pages/about.html', controller : 'About' })
//page2 .when('/date', { templateUrl : 'pages/date.html', controller : 'Date' }); }); |
Sample index.html
|
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title>Single Page App</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="css/bootstrap.min.css"> <link rel="stylesheet" href="css/style.css">
<script src="js/bootstrap.min.js"></script> <script src="bower_components/angular/angular.min.js"></script> <script src="bower_components/angular-route/angular-route.min.js"></script> <script src="js/app.js"></script> <script src="js/controller/controllers.js"></script>
</head> <body ng-app="app">
<a href="#/"><button class="btn btn-danger">Homepage</button></a> <a href="#/about"><button class="btn btn-success">About</button></a> <a href="#/date"><button class="btn btn-warning">Date</button></a>
<div class="row"> <div ng-view> <!-- View goes here --> </div> </div>
</body> </html> |
B.1.1.7 One-way binding vs two-way binding
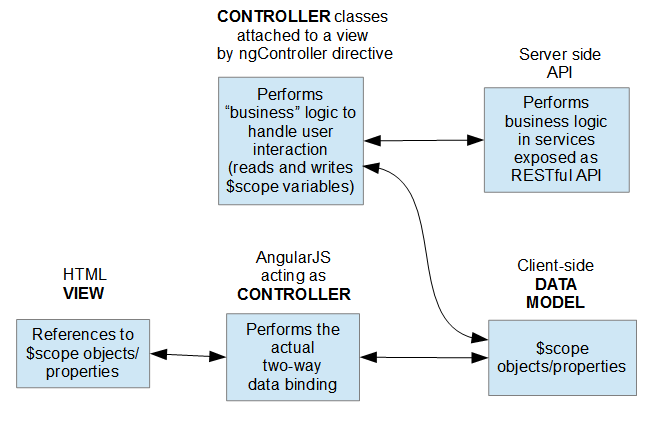
Model: In AngularS, the model provides the pattern responsible for maintaining the data.
View: In AngularJS the view is responsible for displaying all or a portion of the data to the user.
Controller: The controller is a software code that controls all the action between the Model and View.
Sample model data in JSON:
|
<script> $scope.customer = { 'Name' : 'Meraj Ansari', 'Address' : 'Luncknow Road, Faizabad', 'Email' : 'merajansari15gmail.com' 'Contact' : '+919839810502' } </script> |
Sample View line in HTML template
|
<h1> {{customer.name}} </h1> |
Sample Controller to bind Model to View
|
function food($scope){ } |
Call the ng-controller
|
<div ng-controller = "address"> </div> |
Put the MVC together:
|
<!doctype html> <html ng-app> <head> <title>Angular MVC Architecture Course</title> <script src=”https://ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/libs/angularjs/1.6.9/angular.min.js”></script> </head> <body> <div ng-controller = “controller”> <h1>{ {customer.Name} }</h1> </div> <script type=”text/javascript”> function controller($scope){ $scope.customer= { 'Name' : 'John Nguyen', 'Address' : '4753 Montana Dr, Utah', 'Email' : 'JohnNguyen@gmail.com', 'Contact' : '+18018099999' } } </script> </body> </html> |

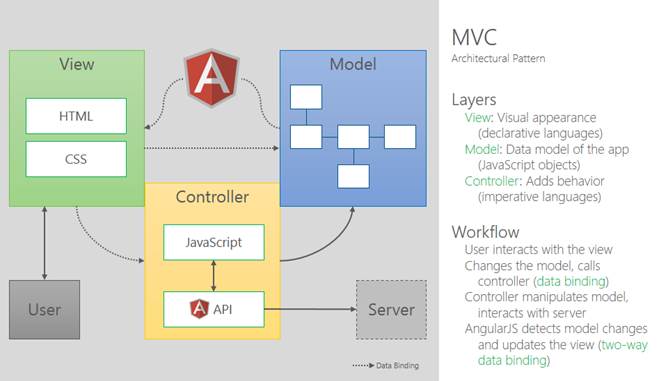
B.1.1.10 Angular : MVC vs MVVM
MVC - Model View Control Design Pattern
HTML
|
<html ng-app="MvcDemoApp"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8" /> <title>Angular MVC Demo</title> </head> <body ng-controller="TextController"> <div><input id="msg" value="{{sampleText}}" /></div> </body> </html> |
CSS
|
#msg { width: 300px; } |
JavaScript
|
var app = angular.module('MvcDemoApp',[]);
app.controller('TextController',['$scope',function($scope){ $scope.sampleText = 'This is an Angular MVC demo.'; }]); |
Put HTML, CSS, and JavaScript together
|
<!DOCTYPE html> <html ng-app> <head> <title>Angular MVC Demo</title> <script type="text/javascript" src="angular.min.js"></script> </head> <body ng-controller="TextController"> <p>{{sampleText}}</p> </body> <script> function TextController($scope) { $scope.sampleText = 'This is an Angular MVC demo.'; } </script> </html> |
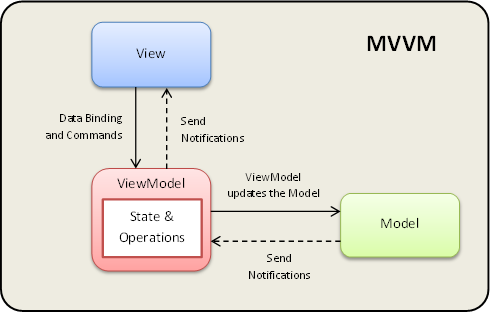
MVVM - Model - View - View Model Design Pattern
HTML
|
<html ng-app="MvvmDemoApp"> <head> <title>Angular MVVM 2-way Binding Demo</title> </head> <body> <h2>Angular MVVM 2-way Binding Demo</h2> <br/> <form ng-controller="MultiplicationController"> <label>Number:</label> <input name="number" ng-change="multiply()" ng-model="data.number"> <label>Number entered by User :</label> {{data.number}} <br> <label>Multiplier:</label> <input name="multiplier " ng-change="multiply()" ng-model="data.multiplier"> <label>Number entered by User :</label> {{data.multiplier}} <br> <label>Result:</label> {{data.result}} </form> </body> </html> |
JavaScript
|
var app = angular.module('MvvmDemoApp',[]);
app.controller('MultiplicationController', ['$scope', function($scope) { $scope.data = {number: 0, multiplier: 0, result: 0}; $scope.multiply = function () { $scope.data.result = $scope.data.number * $scope.data.multiplier; } }]); |
Put HTML, and JavaScript together
|
<html ng-app> <head> <title>Angular MVVM 2-way Binding Demo</title> </head> <body> <h2>Angular MVVM 2-way Binding Demo</h2> <br/> <form ng-controller="MultiplicationController"> <label>Number:</label> <input name="number" ng-change="multiply()" ng-model="data.number"> <label>Number entered by User :</label> {{data.number}} <br> <label>Multiplier:</label> <input name="multiplier" ng-change="multiply()" ng-model="data.multiplier"> <label>Number entered by User :</label> {{data.multiplier}} <br> <label>Result:</label> {{data.result}} </form> </body> <script> function MultiplicationController($scope) { $scope.data = {number: 0, multiplier: 0, result: 0}; $scope.multiply = function() { $scope.data.result = $scope.data.number * $scope.data.multiplier; } } </script> </html> |
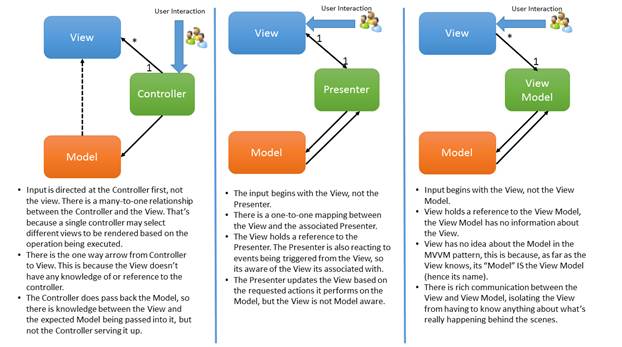
B.1.1.11 Angular: MVC vs MVP vs MVVM
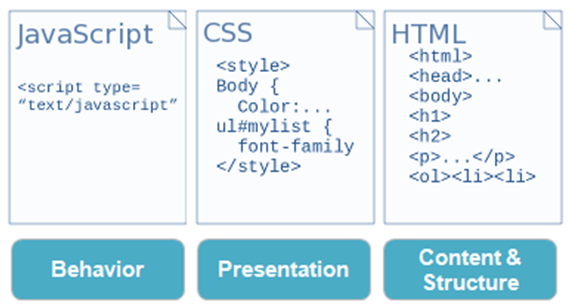
Most of the front-end technology are made up by HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. HTML is responsible for the content & structure of the interface. The CSS is responsible for presentation, and the Javascript is responsible for the behavior.
Basic HTML Structure:
|
<html> <head> <title>website title</title> </head> <body> content of website ... </body> </html> |
Common HTML Tags:
|
<h?> heading </h?> |
Heading (h1 for largest to h6 for smallest) |
|
<p> paragraph </p> |
Paragraph of Text |
|
<b> bold </b> |
Make text between tags bold |
|
<i> italic </i> |
Make text between tags italic |
|
<a href="url"> link name </a> |
Create a link to another page or website |
|
<div> ... </div> |
Divide up page content into sections, and applying styles |
|
<img src="filename.jpg"> |
Show an image |
|
<ul> <li> list </li> </ul> |
Unordered, bullet-point list |
|
<br> |
Line Break (force a new line) |
|
<span style="color:red"> red </span> |
Use CSS style to change text colour |
Common HTML Form:
|
<form> ... </form> |
Form input group decleration |
|
<form> Tag Attributes: |
|
|
action="url" |
URL of Form Script |
|
method="***" |
Method of Form: get, post |
|
enctype="***" |
For File Upload: enctype="multipart/form-data" |
|
<input> ... </input> |
Input field within form |
|
<input> Tag Attributes: |
|
|
type="***" |
Input Field Type: text, password, checkbox, submit etc. |
|
name="***" |
Form Field Name (for form processing script) |
|
value="***" |
Value of Input Field |
|
size="***" |
Field Size |
|
maxlength="?" |
Maximum Length of Input Field Data |
|
checked |
Mark selected field in radio button group or checkbox |
|
<select> ... </select> |
Select options from drop down list |
|
<select> Tag Attributes: |
|
|
name="***" |
Drop Down Combo-Box Name (for form processing script) |
|
size="?" |
Number of selectable options |
|
multiple |
Allow multiple selections |
|
<option> ... </option> |
Option (item) within drop down list |
|
<option> Tag Attributes: |
|
|
value="***" |
Option Value |
|
selected |
Set option as default selected option |
|
<textarea> ... </textarea> |
Large area for text input |
|
<textarea> Tag Attributes: |
|
|
name="***" |
Text Area Name (for form processing script) |
|
rows="?" |
Number of rows of text shown |
|
cols="?" |
Number of columns (characters per rows) |
|
wrap="***" |
Word Wrapping: off, hard, soft |
Common HTML Text Formatting
|
<h?> ... </h?> |
Heading (?= 1 for largest to 6 for smallest, eg h1) |
|
<b> ... </b> |
Bold Text |
|
<i> ... </i> |
Italic Text |
|
<u> ... </u> |
Underline Text |
|
<strike> ... </strike> |
Strikeout |
|
<sup> ... </sup> |
Superscript - Smaller text placed below normal text |
|
<sub> ... </sub> |
Subscript - Smaller text placed below normal text |
|
<small> ... </small> |
Small - Fineprint size text |
|
<tt> ... </tt> |
Typewriter Text |
|
<pre> ... </pre> |
Pre-formatted Text |
|
<blockquote> ... </blockquote> |
Text Block Quote |
|
<strong> ... </strong> |
Strong - Shown as Bold in most browsers |
|
<em> ... </em> |
Emphasis - Shown as Italics in most browsers |
Common HTML Lists formatting
|
<ol> ... </ol> |
Ordered List |
|
<ul> ... </ul> |
Un-ordered List |
|
<li> ... </li> |
List Item (within ordered or unordered) |
|
<ol type="?"> |
Ordered list type: A, a, I, i, 1 |
|
<ol start="??"> |
Ordered list starting value |
|
<ul type="?"> |
Unordered list bullet type: disc, circle, square |
|
<li value="??"> |
List Item Value (changes current and subsequent items) |
|
<li type="??"> |
List Item Type (changes only current item) |
|
<dl> ... </dl> |
Definition List |
|
<dt> ... </dt> |
Term or phrase being defined |
|
<dd> ... </dd> |
Detailed Definition of term |
Using an External CSS File in HTML file
|
<head> <link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="style.css" title="style"> </head> |
Using an CSS within the HTML header
|
<head> <style type="text/css"> h1 { color:red; } </style> </head> |
CSS in the HTML
|
<p style="color:red;">Some red text</p> |
Common CSS Colours & Borders
|
color: red; |
Element colour - eg. red | #FF0000 |
|
background-color: white; |
Background colour of element |
|
background-image: url(image.gif); |
Background colour of element |
|
border-color: yellow; |
Border colour of element |
|
border: 1px solid blue; |
Width, style and colour of border defined together |
Common CSS Text Styles
|
text-align: left; |
Horizontal Alignment - left | center | right |
|
text-decoration: underline; |
Text Decorations - eg. none | underline | line-through |
|
font-family: fontname; |
Font Face (Typeface) - eg. Verdana, Arial, Helvetica |
|
font-size: 16pt; |
Font Size or Height - eg. 12pt | 15px |
|
font-weight: bold; |
Font Weight (Boldness) - eg. bold | normal | 200 |
Commn Size and Layout
|
width: 400px; |
Width of HTML element - eg. 100px | 50% |
|
height: 100%; |
Height of HTML element - eg. 20px | 100% |
|
margin: 5px; |
Margin - space around an element, or distance between two elements |
|
margin-top: 1px; |
Top Margin. Also try -bottom: -left: or -right: |
|
padding: 5px; |
Padding - distance between an elements contents and its border |
|
padding-top: 1px; |
Top Padding. Also try -bottom: -left: or -right: |
Sample JavaScript & HTML: "onClick" calling a Text Alert function
|
<html> <head> <script type="text/javascript"> function functionOne() { alert('You clicked the top text'); } function functionTwo() { alert('You clicked the bottom text'); } </script> </head> <body> <p><a href="#" onClick="functionOne();">Top Text</a></p> <p><a href="javascript:functionTwo();">Bottom Text</a></p> </body> </html> |
Sample JavaScript Onclick:
|
<button onclick="this.innerHTML = Date()">The time is?</button> |
Common HTML Events
|
onchange |
An HTML element has been changed |
|
onclick |
The user clicks an HTML element |
|
onmouseover |
The user moves the mouse over an HTML element |
|
onmouseout |
The user moves the mouse away from an HTML element |
|
onkeydown |
The user pushes a keyboard key |
|
onload |
The browser has finished loading the page |
C.2 Python - Data Structure and Algorithm
Mutable, ordered series, traditionally of the same type of object.
Advantages: Mutable and ordered. Easy to
understand. Relatively efficient memory usage.
Disadvantages: Searching is O(n).
|
To create a list, use square brackets: mylist = [1,2,3] mylist = ['a', 'b', 'c', [1,2,3] ] # 4 elements
x = mylist[3]
Checking membership 3 in mylist # True or False
Sorting mylist = ['d', 'a', 'c', 'b'] mylist.sort() # Returns None mylist # ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd']
Reversing mylist = ['a', 'b', 'c'] mylist.reverse() # returns None mylist # ['c', 'b', 'a'] |
List Methods
|
append() |
Adds an element at the end of the list |
|
clear() |
Removes all the elements from the list |
|
copy() |
Returns a copy of the list |
|
count() |
Returns the number of elements with the specified value |
|
extend() |
Add the elements of a list (or any iterable), to the end of the current list |
|
index() |
Returns the index of the first element with the specified value |
|
insert() |
Adds an element at the specified position |
|
pop() |
Removes the element at the specified position |
|
remove() |
Removes the item with the specified value |
|
reverse() |
Reverses the order of the list |
|
sort() |
Sorts the list |
Mutable, unordered, unique objects. Elements must be hashable.
Advantages: Searching is O(1). Lots of useful methods.
Disadvantages: Not ordered. Elements must be hashable.
|
Creating s = {1,2,3} # Python 2.7, 3.x
Creating from another type s = set([1,2,3]) # From list s = set((1,2,3)) # From tuple s = set('abc') # From string
Adding a value s = {1,2,3} s.add(4) s # {1,2,3,4} s.add(4) s # {1,2,3,4} ��" duplicates are ignored
Adding multiple values s = {1,2,3} s.update([3,4,5]) # Any iterable will do s # {1,2,3,4,5} ��" duplicates ignored
Removing an element s = {1,2,3} s.remove(1) s # {2,3} |
Set Methods
|
add() |
Adds an element to the set |
|
clear() |
Removes all the elements from the set |
|
copy() |
Returns a copy of the set |
|
difference() |
Returns a set containing the difference between two or more sets |
|
difference_update() |
Removes the items in this set that are also included in another, specified set |
|
discard() |
Remove the specified item |
|
intersection() |
Returns a set, that is the intersection of two other sets |
|
intersection_update() |
Removes the items in this set that are not present in other, specified set(s) |
|
isdisjoint() |
Returns whether two sets have a intersection or not |
|
issubset() |
Returns whether another set contains this set or not |
|
issuperset() |
Returns whether this set contains another set or not |
|
pop() |
Removes an element from the set |
|
remove() |
Removes the specified element |
|
symmetric_difference() |
Returns a set with the symmetric differences of two sets |
|
symmetric_difference_update() |
inserts the symmetric differences from this set and another |
|
union() |
Return a set containing the union of sets |
|
update() |
Update the set with the union of this set and others |
Immutable, ordered series traditionally containing different objects
Advantages: Immutable and ordered. Relatively efficient memory usage (more
than lists).
Disadvantages: Searching is O(n). Hard to understand for many
Python newcomers.
|
Creating t = ('a', 1, [1,2,3]) # () and comma indicate tuple t = ('a',) # single-element tuple requires ,!
From another type tuple([1,2,3]) # (1,2,3)
Iterating over the elements t = ('a', 'b', 'c') for item in t: print(item)
Iterating over the sorted elements t = ('d', 'a', 'c', 'b') for item in sorted(t): print(item) |
Tuples Methods
|
count() |
Returns the number of times a specified value occurs in a tuple |
|
index() |
Searches the tuple for a specified value and returns the position of where it was found |
Mutable, unordered pairs (keys and values) of objects. Keys must be hashable.
Advantages: O(1) searching for keys. Makes it easy to create trees and other
hierarchical data structures. Can be used to create self-documenting code. Many
problems can be described in terms of key-value pairs.
Disadvantages: Only lookup by key. Uses more memory than lists
and tuples. Keys must be hashable.
|
Creating {'a':1, 'b':2, 'c':3} # {'a': 1, 'b': 2, 'c': 3}
Creating from other data dict(['a',1], ['b',2], ['c',3]) # {'a': 1, 'b': 2, 'c': 3} dict(('a',1), ('b',2), ('c',3)) # {'a': 1, 'b': 2, 'c': 3}
Retrieving from a key d = {'a':1, 'b':2, 'c':3} d['a'] # 1 d['z'] # raises KeyError
Add a key-value pair d = {'a':1, 'b':2, 'c':3} d['d'] = 100 d # {'a': 100, 'b': 2, 'c': 3, 'd': 100}
Replacing an existing value d = {'a':1, 'b':2, 'c':3} d['a'] = 100 d # {'a': 100, 'b': 2, 'c': 3}
Replacing multiple existing values d = {'a':1, 'b':2 } x = {'a':555, 'z':987} d.update(x, y=10) # Returns None d # {'a': 555, 'b': 2, 'y': 10, 'z': 987}
Removing an element d = {'a':1, 'b':2, 'c':3} del(d['a']) d # {'c': 3, 'b': 2}
Getting the keys d = {'a':1, 'b':2, 'c':3} d.keys() # ['a', 'c', 'b'] (Python 2) d.keys() # dict_keys(['a', 'b', 'c']) (Python 3)
Getting the values d = {'a':1, 'b':2, 'c':3} d.values() # [1, 2, 3] (Python 2) d.values() # dict_values([1, 2, 3]) (Python 3)
Iterating over the keys d = {'a':1, 'b':2, 'c':3} for k in d: print("{0}: {1}".format(k, d[k]))
Iterating over the pairs d = {'a':1, 'b':2, 'c':3} for k, v in d.items() print("{0}: {1}".format(k, v)
Iterating over the sorted keys d = {'a':1, 'b':2, 'c':3} for k in sorted(d): print("{0}: {1}".format(k, d[k])) |
Dictionary Methods
|
clear() |
Removes all the elements from the dictionary |
|
copy() |
Returns a copy of the dictionary |
|
fromkeys() |
Returns a dictionary with the specified keys and value |
|
get() |
Returns the value of the specified key |
|
items() |
Returns a list containing a tuple for each key value pair |
|
keys() |
Returns a list containing the dictionary's keys |
|
pop() |
Removes the element with the specified key |
|
popitem() |
Removes the last inserted key-value pair |
|
setdefault() |
Returns the value of the specified key. If the key does not exist: insert the key, with the specified value |
|
update() |
Updates the dictionary with the specified key-value pairs |
|
values() |
Returns a list of all the values in the dictionary |
Sample String
|
a = "Hello, World!" print(a.split(",")) # returns ['Hello', ' World!'] |
String Methods
|
capitalize() |
Converts the first character to upper case |
|
casefold() |
Converts string into lower case |
|
center() |
Returns a centered string |
|
count() |
Returns the number of times a specified value occurs in a string |
|
encode() |
Returns an encoded version of the string |
|
endswith() |
Returns true if the string ends with the specified value |
|
expandtabs() |
Sets the tab size of the string |
|
find() |
Searches the string for a specified value and returns the position of where it was found |
|
format() |
Formats specified values in a string |
|
format_map() |
Formats specified values in a string |
|
index() |
Searches the string for a specified value and returns the position of where it was found |
|
isalnum() |
Returns True if all characters in the string are alphanumeric |
|
isalpha() |
Returns True if all characters in the string are in the alphabet |
|
isdecimal() |
Returns True if all characters in the string are decimals |
|
isdigit() |
Returns True if all characters in the string are digits |
|
isidentifier() |
Returns True if the string is an identifier |
|
islower() |
Returns True if all characters in the string are lower case |
|
isnumeric() |
Returns True if all characters in the string are numeric |
|
isprintable() |
Returns True if all characters in the string are printable |
|
isspace() |
Returns True if all characters in the string are whitespaces |
|
istitle() |
Returns True if the string follows the rules of a title |
|
isupper() |
Returns True if all characters in the string are upper case |
|
join() |
Joins the elements of an iterable to the end of the string |
|
ljust() |
Returns a left justified version of the string |
|
lower() |
Converts a string into lower case |
|
lstrip() |
Returns a left trim version of the string |
|
maketrans() |
Returns a translation table to be used in translations |
|
partition() |
Returns a tuple where the string is parted into three parts |
|
replace() |
Returns a string where a specified value is replaced with a specified value |
|
rfind() |
Searches the string for a specified value and returns the last position of where it was found |
|
rindex() |
Searches the string for a specified value and returns the last position of where it was found |
|
rjust() |
Returns a right justified version of the string |
|
rpartition() |
Returns a tuple where the string is parted into three parts |
|
rsplit() |
Splits the string at the specified separator, and returns a list |
|
rstrip() |
Returns a right trim version of the string |
|
split() |
Splits the string at the specified separator, and returns a list |
|
splitlines() |
Splits the string at line breaks and returns a list |
|
startswith() |
Returns true if the string starts with the specified value |
|
strip() |
Returns a trimmed version of the string |
|
swapcase() |
Swaps cases, lower case becomes upper case and vice versa |
|
title() |
Converts the first character of each word to upper case |
|
translate() |
Returns a translated string |
|
upper() |
Converts a string into upper case |
|
zfill() |
Fills the string with a specified number of 0 values at the beginning |
D RESTful API: Front End and Back End Integration
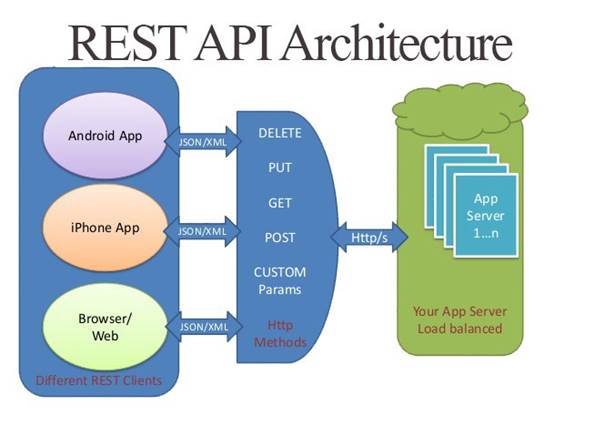
Simple HTML form to submit to the API
|
<form action="" method="post"> <input type="text" name="name" placeholder="Enter Your Name"> <button>Submit</button> <form> |
Pythn/Flask API to handle API call:
|
from flask import Flask, render_template, request @app.route("/hello", methods=["POST"]) def hello(): name = request.form.get("name") return render_template("hello.html", name=name) |
|
HTTP Verb |
CRUD |
Entire Collection (e.g. /customers) |
Specific Item (e.g. /customers/{id}) |
|
POST |
Create |
201 (Created), 'Location' header with link to /customers/{id} containing new ID. |
404 (Not Found), 409 (Conflict) if resource already exists.. |
|
GET |
Read |
200 (OK), list of customers. Use pagination, sorting and filtering to navigate big lists. |
200 (OK), single customer. 404 (Not Found), if ID not found or invalid. |
|
PUT |
Update/Replace |
405 (Method Not Allowed), unless you want to update/replace every resource in the entire collection. |
200 (OK) or 204 (No Content). 404 (Not Found), if ID not found or invalid. |
|
PATCH |
Update/Modify |
405 (Method Not Allowed), unless you want to modify the collection itself. |
200 (OK) or 204 (No Content). 404 (Not Found), if ID not found or invalid. |
|
DELETE |
Delete |
405 (Method Not Allowed), unless you want to delete the whole collection—not often desirable. |
200 (OK). 404 (Not Found), if ID not found or invalid. |
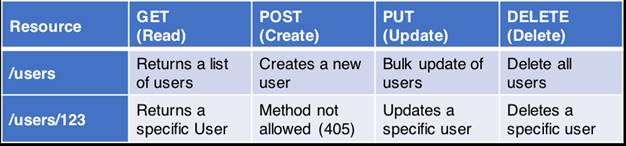
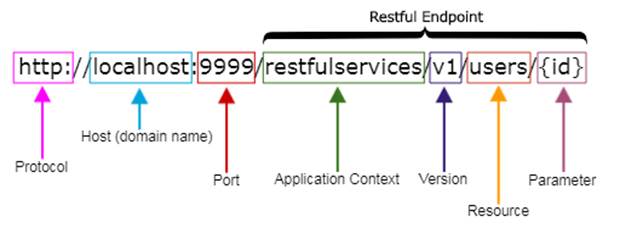
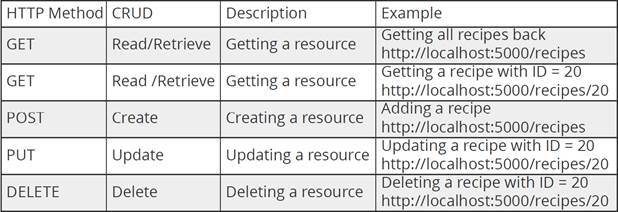
JSON can easily parsed into a ready-to-use JavaScript object. XML is much more difficult to parse than JSON.
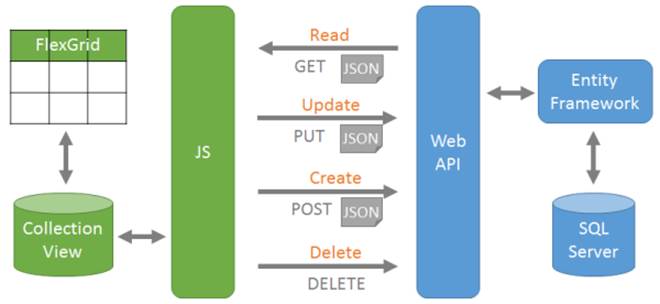

Common SQL operations:
|
SELECT |
SELECT * FROM flights ORDER BY duration ASC; |
|
INSERT |
INSERT INTO flights (origin, destination, duration) VALUES ('New York', 'Boston', 693); |
|
UPDATE |
UPDATE flights SET duration = 872 WHERE origin = 'New York' AND destination = 'Boston'; |
|
DELETE |
DELETE FROM flights WHERE destination = 'Boston' |
JOIN : Compound Queries
|
JOIN |
SELECT origin, destination, name FROM flights JOIN passengers ON passengers.flight_id = flights.id; |
|
JOIN & WHERE |
SELECT origin, destination, name FROM flights JOIN passengers |
Other Common SQL operations:
|
Create TABLE |
CREATE TABLE table_name (column_1 datatype, column_2 datatype, column_3 datatype); |
create a new table in a database |
|
ALTER table |
ALTER TABLE table_name ADD column_name datatype; |
add columns to a table in a database |
|
COUNT |
SELECT COUNT(column_name) FROM table_name; |
counts the number of rows when the column is not NUL |
|
BETWEEN |
SELECT column_name(s) FROM table_name WHERE column_name |
filter the result within a certain range |
|
INNER JOIN |
SELECT column_name(s) FROM table_1 JOIN table_2 |
combine rows from different tables if the Join condition goes TRUE |
|
OUTER JOIN |
SELECT column_name(s) FROM table_1 LEFT JOIN table_2 |
combine rows from different tables even if the condition is NOT TRUE |
|
AVG |
SELECT AVG(column_name) FROM table_name; |
aggregate a numeric column and return its average |
|
SUM |
SELECT SUM(column_name) FROM table_name; |
return sum of values from a particular column |
|
SELECT DISTINCT |
SELECT DISTINCT column_name FROM table_name; |
returns unique values in specified columns |
https://www.listendata.com/2018/12/javascript-shiny-r.html
https://www.designveloper.com/full-stack-engineer/
https://medium.com/@dilankam/restful-api-design-best-practices-principles-ded471f573f3
http://www.simplehtmlguide.com/
https://www.w3schools.com/
https://cs50.harvard.edu/
https://packtpub.com
https://www.edialliance.com/
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/13067607/angularjs-client-mvc-pattern
https://tutorialseye.com/angularjs-mvc-architecture.html
https://www.slideshare.net/igortalevski1/angularjs-1x-your-first-application-problems-and-solutions