Docker Containter
1
What & why is Docker?............................................................................................................. 2
1.1 RAM -
Memory.................................................................................................................... 2
1.2 Size
& Startup...................................................................................................................... 2
1.3
Integration........................................................................................................................... 3
1.4 Docker
Engine...................................................................................................................... 3
1.4.1
Docker Image................................................................................................................ 4
1.4.2
Docker container.......................................................................................................... 5
1.4.3
Docker registry............................................................................................................. 5
1.5 Docker
Architecture............................................................................................................ 5
2 Docker
tutorial........................................................................................................................... 6
2.1
Pull/Run/Stop/delete Docker Hello world....................................................................... 6
2.2 Run
first Alpine Linux container........................................................................................ 7
2.3 Run
Webapps with Docker................................................................................................. 8
3 Build
Docker Image with Dockerfile......................................................................................... 9
3.1 What is
Dockerfile............................................................................................................... 9
3.2
Dockerfile Basic commands............................................................................................... 9
3.2.1
Create Python-Flask-Webapps image with Dockerfile........................................... 10
3.2.2 Push
your Docker mage to Docker cloud................................................................ 13
4 Reference.................................................................................................................................. 14
1 What &
why is Docker?
Docker is software that offers a set of
platform-as-a-service products for developing and deploying applications by
packaging software in containers.
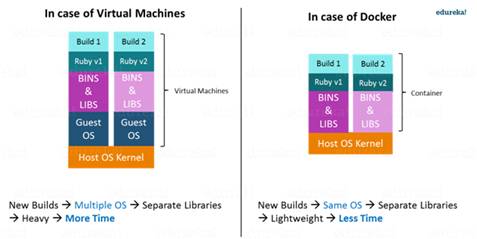
Container is lightweight, portable, virtual environments that developers can
share without risking inconsistencies in development. Many organization
are switching from using virtual machine to Docker
containers.
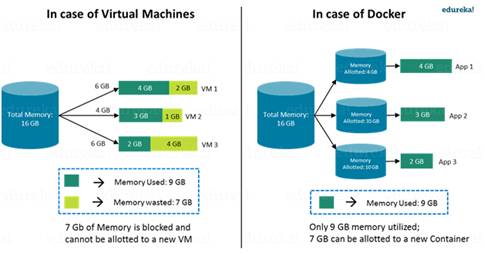
Docker using less memory than virtual
machine as there is no need to run guest OS.
Docker start-up faster as there is no
need to load and run guest OS.
Docker make it easier for developer to focus on coding rather than guest
OS.
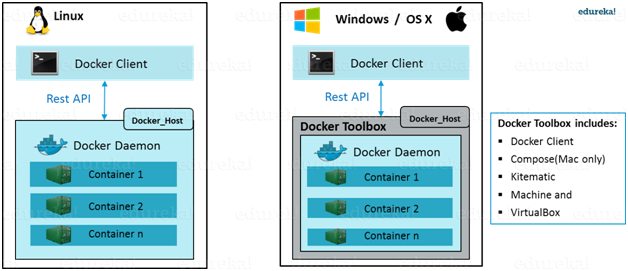
1.4 Docker Engine
Docker engine is the application that is
installed on host machine. It works like client-server application:
- A server which is a type of long-running program called a
daemon process.
- A command line interface (CLI) client.
- REST API is used for communication between the CLI client and Docker Daemon.
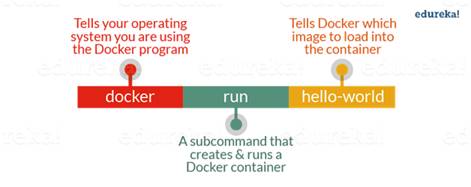
1.4.1 Docker Image
Docker Image is a template which is used
to create docker containers. They are building block
of docker container.
Docker let people create and share
software through docker image, and we don't need to
worry about compatibility, the docker container can alway run it.
The docker Image is create using build command.
the read only templates is used for
creating container by using the run command.
We can either use a ready-made docker
image from docker-hub or create a new image as per
requirement.
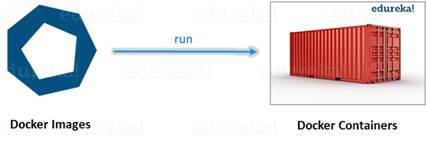
1.4.2 Docker container
Docker container is a ready application
created from Docker Image, or we can say it is
running instances of the Image and they hold the entire package needed to run
the application.
1.4.3 Docker registry
Docker registry is where the Docker Image is stored, the
registry can be our local computer, or public repository like Docker Hub where multiple users can collaborate in building
an application.
Docker Hub allow
multple team within a organization to upload, share,
and exchange Docker Image.
1.5 Docker Architecture
Docker Architecture: include 4 components
1) Docker client: user can use CLI to trigger Docker command.
2) Docker Host: run the Docker
Daemon.
3) Docker Registry: storing Docker
Images.
4) Docker Doemon:
running inside Docker Host and responsible for images
and containers.
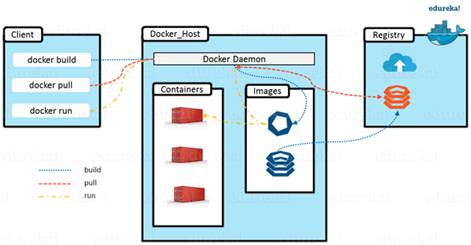
Docker Lifecycle:
1) Client use CLI to issue a command (Build/Pull/Run) to Docker Daemon.
2) Docker Daemon build
an image based on your CLI command and save it to Registry (which can be locally
or at Docker hub).
3) If Client donot want to build an
Image, they pull it from Docker hub, which was built
by another user.
4) Client can create a running instance of the Docker Image by issue a run command from the CLI, which
will create a new running container.
2 Docker tutorial
2.1 Pull/Run/Stop/delete
Docker Hello world
Pull
the Docker Image hello-world from Docker
hub:
|
$ docker pull hello-world |
List
all the docker images in your computer:
|
$ docker images |
Run the
Docker hello-world:
|
$ docker run hello-world >> Hello world from Docker! |
stop
all docker container:
|
$ docker container prune |
remove docker image:
|
$ docker image rm hello-world -f |
2.2 Run first
Alpine Linux container
Pull alpine image
|
$ docker pull alpine |
Run alpine container from docker
image
|
$ docker run alpine |
Run linux command list folder
command "Ls -s" inside docker
|
$ docker run alpine ls -l |
Run echo "hello from alpine" command inside
container
|
$ docker run alpine echo
"hello from alpine" |
List all currently running container
|
$ docker ps |
List all the container command had ran in the past
|
$ docker ps -a |
2.3 Run Webapps with Docker
Pull sample docker static site
image
|
$ docker pull sample |
Run docker sample site
|
docker run dockersamples/static-site |
The webapp is running, but we cannot access it because there is
no port to access the webapp from the browser, so let
stop the container and configure the port
|
look up the container that is currently running: and
get the ID of container $ docker ps then kill the container by the ID $ docker stop ID delete the container by the ID $ docker rm
ID |
now,
let run the container in detached mode
|
$ docker run --name
static-site -e AUTHOR="Your Name" -d -P dockersamples/static-site -d: will create a container with the process
detached from your terminal -p: will publish all the exposed container ports to
random ports on the Docker host -e: is how you pass environment variables to the
container --name: allows you to specify a container name AUTHOR: is the environment variable name and Your
Name is the value that you can pass |
check the docker
port command:
|
$ docker port static-site 443/tcp ->
0.0.0.0:49153 80/tcp -> 0.0.0.0:49154 |
the site should be available at:
http://localhost:49154/
3 Build Docker Image with Dockerfile
3.1 What is Dockerfile
Dockerfile is a simple text file with a set
of command or instruction to create a docker image, we can use dockerfile to
create a new docker image when the existing docker images won't meet our requirement.
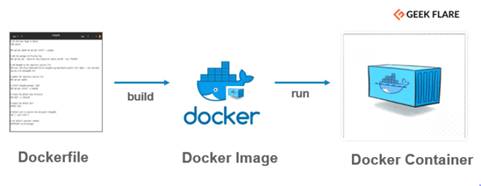
Step to
create and run new docker container:
1) create a dockerfile
contain instruction to create a new docker image.
2) Run docker command to build new docker image
3) Run "docker run"
command to create and run new container from docker
image.
3.2 Dockerfile Basic commands
FROM – Defines
the base image to use and start the build process.
RUN – It takes
the command and its arguments to run it from the image.
CMD – Similar
function as a RUN command, but it gets executed only after the container is
instantiated.
ENTRYPOINT – It targets
your default application in the image when the container is created.
ADD – It
copies the files from source to destination (inside the container).
ENV – Sets
environment variables.
3.2.1 Create
Python-Flask-Webapps image with Dockerfile
1) pull a ubuntu:12.04
|
docker pull
ubuntu:12.04 |
2) Create app.py
|
from flask import Flask, render_template import random app = Flask(__name__) # list of cat images images = [
"http://img.buzzfeed.com/buzzfeed-static/static/2013-10/enhanced/webdr05/15/9/anigif_enhanced-buzz-26388-1381844103-11.gif",
"http://img.buzzfeed.com/buzzfeed-static/static/2013-10/enhanced/webdr01/15/9/anigif_enhanced-buzz-31540-1381844535-8.gif",
"http://img.buzzfeed.com/buzzfeed-static/static/2013-10/enhanced/webdr05/15/9/anigif_enhanced-buzz-26390-1381844163-18.gif",
"http://img.buzzfeed.com/buzzfeed-static/static/2013-10/enhanced/webdr06/15/10/anigif_enhanced-buzz-1376-1381846217-0.gif",
"http://img.buzzfeed.com/buzzfeed-static/static/2013-10/enhanced/webdr03/15/9/anigif_enhanced-buzz-3391-1381844336-26.gif",
"http://img.buzzfeed.com/buzzfeed-static/static/2013-10/enhanced/webdr06/15/10/anigif_enhanced-buzz-29111-1381845968-0.gif",
"http://img.buzzfeed.com/buzzfeed-static/static/2013-10/enhanced/webdr03/15/9/anigif_enhanced-buzz-3409-1381844582-13.gif",
"http://img.buzzfeed.com/buzzfeed-static/static/2013-10/enhanced/webdr02/15/9/anigif_enhanced-buzz-19667-1381844937-10.gif",
"http://img.buzzfeed.com/buzzfeed-static/static/2013-10/enhanced/webdr05/15/9/anigif_enhanced-buzz-26358-1381845043-13.gif",
"http://img.buzzfeed.com/buzzfeed-static/static/2013-10/enhanced/webdr06/15/9/anigif_enhanced-buzz-18774-1381844645-6.gif",
"http://img.buzzfeed.com/buzzfeed-static/static/2013-10/enhanced/webdr06/15/9/anigif_enhanced-buzz-25158-1381844793-0.gif",
"http://img.buzzfeed.com/buzzfeed-static/static/2013-10/enhanced/webdr03/15/10/anigif_enhanced-buzz-11980-1381846269-1.gif" ] @app.route('/') def index(): url = random.choice(images) return render_template('index.html', url=url) if __name__ == "__main__": app.run(host="0.0.0.0") |
3) Create requirements.txt
|
Flask==0.10.1 |
4) Create templates/index.html
|
<html> <head> <style
type="text/css"> body {
background: black; color:
white; } div.container {
max-width: 500px;
margin: 100px auto;
border: 20px solid white;
padding: 10px; text-align:
center; } h4 {
text-transform: uppercase; }
</style>
</head> <body> <div
class="container">
<h4>Cat Gif of the day</h4> <img src="{{url}}" />
<p><small>Courtesy: <a
href="http://www.buzzfeed.com/copyranter/the-best-cat-gif-post-in-the-history-of-cat-gifs">Buzzfeed</a></small></p>
</div>
</body> </html> |
4) Create Dockerfile
|
# our base image FROM alpine:3.5 # Install python and pip RUN apk add --update py2-pip # install Python modules needed by the Python app COPY requirements.txt /usr/src/app/ RUN pip install --no-cache-dir -r /usr/src/app/requirements.txt # copy files required for the app to run COPY app.py /usr/src/app/ COPY templates/index.html /usr/src/app/templates/ # tell the port number the container should expose EXPOSE 5000 # run the application CMD ["python", "/usr/src/app/app.py"] |
5) build Docker
myfirstapp by run docker
build cmd:
|
$ docker
build -t myfirstapp . |
6) Run docker image myfirstapp just got built by dockerfile
|
$ docker run -p 8888:5000 myfirstapp |
7) open browser at:
http://localhost:8888/
3.2.2 Push your Docker mage to Docker cloud
1) login your docker
account from cmd:
|
docker login |
2) push docker
image to cloud
|
docker push YOUR_USERNAME/myfirstapp |
3) stop and remove docker image off your local computer:
|
$ docker stop myfirstapp $ docker rm myfirstapp |
https://www.edureka.co/blog/what-is-docker-container
https://geekflare.com/dockerfile-tutorial/
https://www.docker.com/resources/what-container
https://docs.docker.com/engine/reference/commandline/container/